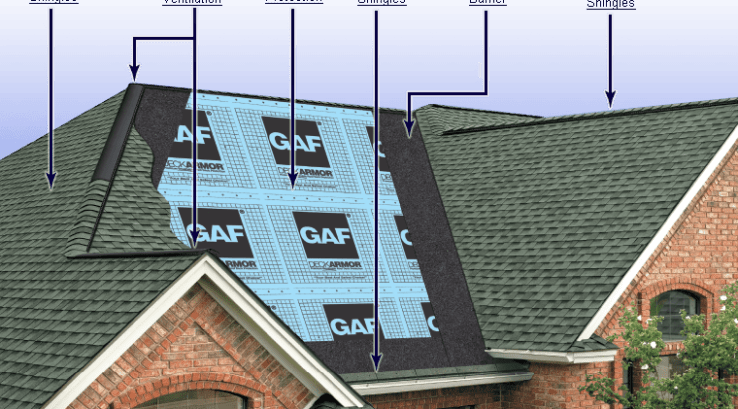
Whether repairing or replacing your roof, learning the common terminology and parts of a roof used by contractors can help you better understand the roofing process. The roof terms outlined in this guide will allow you to keep up with your contractor and decide on the appropriate roofing project for your property.
Roofing Terms
Asphalt: A bituminous substance obtained after petroleum or crude oil processing and used for waterproofing in different roof types.
Asphalt Roof Cement: Mud-like mixture of stabilizers, fillers, and asphalt used in roofing.
Apron Flashing: Refers to the flashing applied where a sloped roof intersects with a chimney, another roof section, or a vertical wall.
Asphalt Primer: A thin bituminous liquid applied on a surface to absorb dust and enhance self-adhering membrane adhesion.
Buckling: Rippling or wrinkling that changes the shape of underlay or shingles due to the roof deck’s movement and is common in board decks.
Blistering: Describes Bubbles that may occur on asphalt roofing’s surface after installation.
Cricket: A peaked saddle creation at the chimney’s back used to deflect water from the chimney and prevent ice and snow accumulation.
Deck: The wood plank layer or plywood supporting the entire roof system.
Dormer: A framed or raised roof section that protrudes from the entire roof.
Downspout: Refers to a conduit for directing water from the building walls and the roof to channel it to the ground.
Drip Edge: A material strip installed along the roof’s edges to prevent water from dripping onto the deck, siding, and eaves.
Eave: The roof edges that project beyond the outer wall.
Exposure: The roofing portion that is exposed to weather following installation.
Fascia: A wooden board beside the roof edge where gutters hang off.
Fiberglass Mat: Asphalt roofing shingle material obtained from glass fibers.
Flashing: Metal pieces used to hamper water seepage into a building around any projection or intersection in a roof.
Flashing Cement: A unique stabilizer or bitumen mixture used for sealing flashing areas.
Gable: The upper part of a building’s exterior wall that forms a triangular point at a sloping roof’s ridge.
Gable Roof: A traditional roofing design comprising two peaked planes forming a triangle at the meeting point.
Granules: Composite material obtained from crushed gravel or stone used to surface asphalt for protection against UV rays.
Gutter: A water channel installed around the roof edge to direct runoff water toward the drains or downspouts.
Gambrel Roof: A roof type with two sloping planes whereby each ridge has different pitches. The lower plane’s slope is steeper than the upper, and each end contains a gable.
Hand-sealing: Allows roofers to check if shingles have been sealed appropriately and to apply additional adhesive if necessary.
Hip Roof: A sloped roof rising on all four sides and meeting at the top. Most hip roofs flatten at the peak, but a square hip roof is pyramid shaped.
Ice Dam: A snow or ice accumulation caused by hot air escaping from the roof and gutter blockage. The heat coming from the building melts the snow and ice, forcing it into the roofing system as it can’t leave through the gutter.
Impact Resistance: A roofing material’s strength against construction equipment, foot traffic, and falling objects.
Interlocking Shingles: Individual shingles that fasten together to offer better-quality resistance against wind.
Insulation: Roofing materials that trap heat in a building and let cold air out.
Laminate Shingles: Shingles created from separate pieces that are laminated together. They are also called architectural or dimensional shingles.